



Making a Radiation Treatment Plan
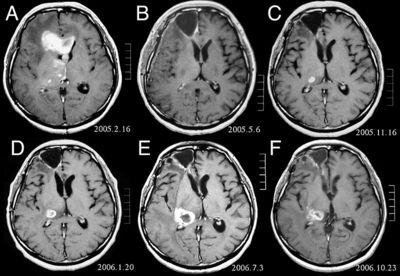
Work-up and diagnosis
By the time a patient sees the Radiation Oncologist the diagnosis of cancer has usually been made and the role for radiation is being considered.
Once the decision to proceed with radiation treatment has been made a treatment plan must be made. This is a complex process that involves many members of the radiation team and begins with a trip to the Simulator.
Radiation simulator
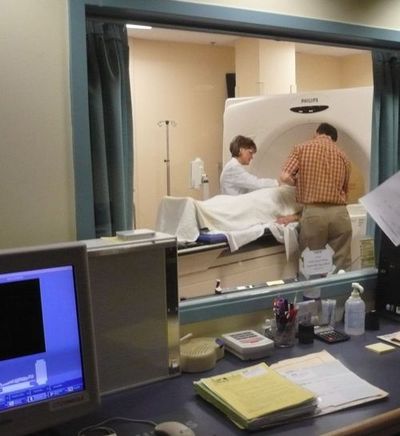
The simulator is a CT scanner with a bed, similar to that of the radiation treatment bed, and a computer interface with the radiation planning software.
During the time in the simulator numerous measurements and images are taken.
This step in the process can be time consuming compared to the actual treatments. It can take anywhere from 15 minutes to more than an hour. Particularly complex plans may require more than one trip to the simulator.
Markings of the treatment area are made with ink and, if required, small tattoos are place in the skin at this time. These are used to help with setting the patient up for subsequent treatments.
People receiving radiation to the head and neck will have a mask made prior to simulation. The mask ensures proper positioning, stillness and allows the markings to be made on the mask rather than the face. The mask can be quite frightening to wear at first, especially for the claustrophobic or patients with airway compromise who are uncomfortable lying flat.

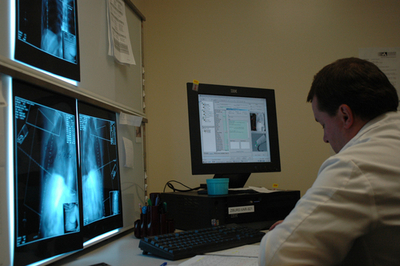
Treatment plan
The radiation treatment plan is created using clinical information, the plain and CT images from the simulator and computer modeling. Dosimetrists, Medical Physicists and Radiation Oncologists are all involved in the creation and confirmation of the treatment plan. The plan is checked prior to each treatment by the Radiation Therapist.
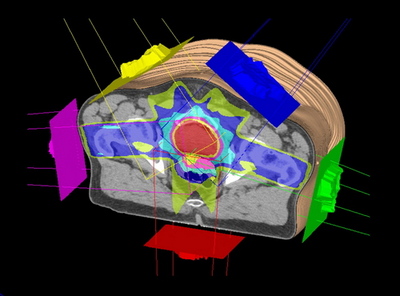
Radiation plan
The Radiation Oncologist takes the images obtained by the Radiation Technologist during the simulation and delineates the tumour contours, safety margins and treatment area.
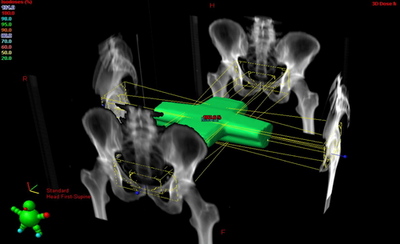
Dosimetry
The Dosimetrists review the radiation plan from the Radiation Oncologist and design beam arrangements to maximize the treatment dose delivered to the tumour and sparing healthy tissue.
These plans are then reviewed by the Radiation Oncologist.
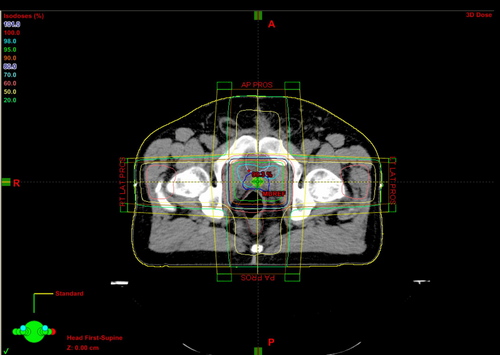
Medical physics
Medical Physicists review the plan that has been created.
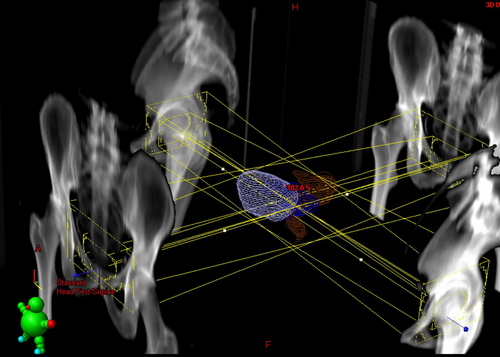
Treatment plan review/approval
The plan is then returned to the Radiation Oncologist for final approval.
 Previous
Previous